Post-Trauma Vision Syndrome (PTVS) is a condition that can affect individuals who have experienced some sort of traumatic event. This condition can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life and can lead to various visual symptoms that can affect one’s ability to perform daily activities.
Despite being a commonly reported issue among individuals who have experienced traumatic events, PTVS is still not widely recognized or understood by the general public.
Understanding the symptoms and effects of PTVS can help individuals who are struggling with it get the support and care they need to manage the condition and improve their quality of life.
What Does Post-Trauma Vision Syndrome Mean?
Post-Trauma Vision Syndrome (PTVS) is a condition that can develop after an individual has experienced a traumatic event such as a car accident, physical assault, sports injury, or any other type of traumatic brain injury. The syndrome can result in a range of visual symptoms that can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life.
PTVS is believed to be caused by damage to the visual system, including the eyes and the part of the brain responsible for processing visual information. This damage can result in changes to the way the brain processes visual information, leading to the symptoms associated with PTVS.
Symptoms of Post-Trauma Vision Syndrome (PTVS)
The symptoms of Post-Traumatic Vision Syndrome (PTVS) can vary from person to person, but some common symptoms include:
- Double vision
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Difficulty with eye movements
- Reduced visual acuity
- Headaches
- Fatigue or eye strain
- Difficulty reading or focusing on close objects
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Disorientation or imbalance
Effects Of Post Trauma Vision Syndrome
Post-Traumatic Vision Syndrome (PTVS) can have a number of effects on an individual’s life, including:
Decreased Living Quality
Post-traumatic vision syndrome (PTVS) can decrease quality of life in several ways. The vision problems associated with PTVS can make everyday tasks, such as driving, reading, or working, difficult or even impossible. This can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression.
Difficulty With Work and Education
Individuals with PTVS may struggle to perform their job duties or attend school if their visual symptoms are affecting their ability to see or read.
Increased Stress And Anxiety Levels
Post-traumatic vision syndrome (PTVS) can increase stress and anxiety levels because it affects an individual’s daily life and ability to perform normal activities. This can lead to feelings of frustration, anger, and hopelessness, which can cause an increase in stress and anxiety.
Additionally, the uncertainty and unpredictability of the condition can also contribute to these feelings, as people with PTVS may worry about losing their vision completely and the impact it will have on their lives. The physical and emotional strain of dealing with the condition can also increase stress and anxiety levels.
Relationship Difficulties
Post-traumatic vision syndrome (PTVS) can have a significant impact on a person’s relationships with others. People who suffer from PTVS may have trouble participating in daily activities and performing tasks that require good vision, leading to difficulties in maintaining social connections and relationships. They may feel isolated and lonely, which can strain relationships with friends and family.
Physical Discomfort
Some common symptoms of PTVS include headaches, eye strain, dizziness, and neck pain. These symptoms can arise from the visual difficulties and challenges that a person experiences with PTVS, such as double vision, blurred vision, light sensitivity, and visual field restrictions.
These difficulties can cause eye fatigue and strain, leading to headaches, neck pain, and dizziness. The physical discomfort associated with PTVS can also be due to changes in posture and eye movements as a person tries to compensate for their vision problems which can result in muscle tension and discomfort.
People Responsible For Treating Post-Traumatic Vision Syndrome (PTVS)
The people responsible for treating post-traumatic vision syndrome (PTVS) are healthcare professionals who specialize in diagnosing and treating eye conditions. This can include optometrists, ophthalmologists, rehabilitation specialists, and therapists.
These individuals use their knowledge and expertise to assess the extent of the condition and develop a customized treatment plan to help individuals recover their vision.
They may use a combination of medical treatments, therapies, and rehabilitation exercises to help people regain control of their lives and overcome PTVS.
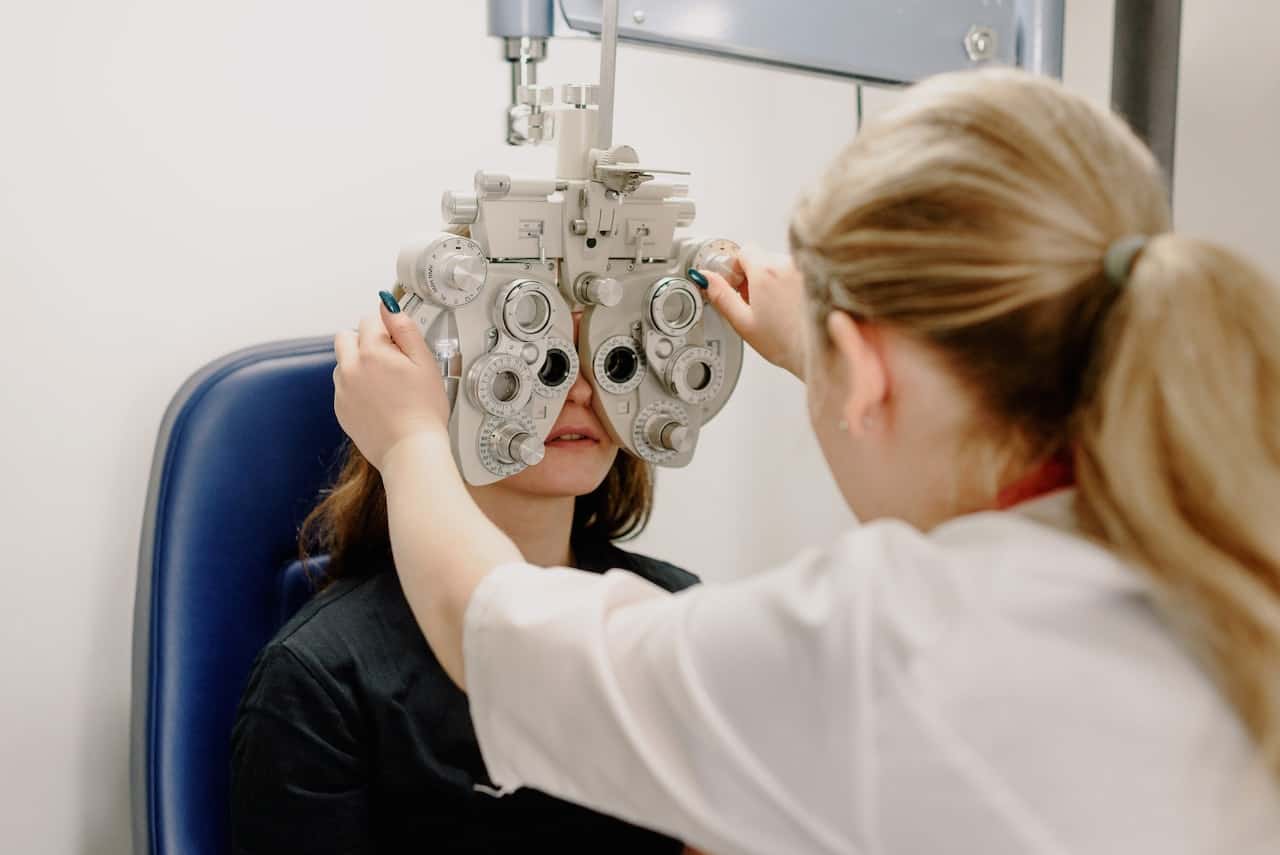
Diagnosis Of Post-Traumatic Vision Syndrome (PTVS)
The diagnosis of PTVS involves a comprehensive eye examination, a review of the patient’s medical history, and an evaluation of the symptoms experienced by the patient.
This may include symptoms such as blurred vision, double vision, headaches, eye strain, difficulty with reading or focusing, and sensitivity to light.
The diagnosis may also involve additional tests, such as visual field testing and scans of the brain and eyes, to determine the extent and cause of the visual problems. The diagnosis of PTVS is important for determining the best course of treatment for the patient.
The Process Of Treating Post-Traumatic Vision Syndrome
The process of treating Post-Traumatic Vision Syndrome (PTVS) can involve several steps, including:
Diagnosis
The first step in treating PTVS is to receive a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional, such as an optometrist or neurologist. This may involve a comprehensive eye exam, neurological testing, and an assessment of the individual’s visual symptoms.
Identifying The Cause
Once PTVS is diagnosed, healthcare professionals will work to identify the underlying cause of the condition and may carry out additional testing or imaging to determine if there are any underlying neurological or physical issues that are contributing to PTVS.
Developing A Treatment Plan
Based on the results of the diagnostic process, a treatment plan will be developed that addresses the individual’s specific needs and goals. This may include vision therapy, physical therapy, medication, or a combination of these interventions.
Vision Therapy
Vision therapy involves a series of exercises designed to improve the visual processing skills of individuals with PTVS. This could entail eye-movement exercises, perceptual training, or the use of special lenses or prisms to help individuals better process visual information.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help individuals with PTVS improve their eye-movement control and reduce symptoms of headaches or eye strain by maybe engaging in exercises that target specific muscle groups and improve coordination and balance.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of PTVS, such as headaches or dizziness.
Psychological Support
Mental health support can be an important component of the treatment process for PTVS, as the condition can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being which involve working with a psychologist or therapist to address any related mental health concerns.
How Long Does The Treatment Of Post Trauma Vision Syndrome Take
The road to recovery from post-traumatic vision syndrome (PTVS) can be a long and winding one, with no two journeys being exactly alike. The length of treatment required to alleviate symptoms can vary greatly, depending on the individual and the severity of their condition.
For those who are lucky enough to experience only mild to moderate symptoms, a few months of proper care and treatment can often bring about improvement.
However, for those who suffer from more severe cases of PTVS, the road to recovery can be a much longer one, taking several months or even a year or more to fully overcome.
Despite the uncertainty of the treatment time, it’s important to remember that with patience, dedication, and a strong support system, anyone can overcome PTVS and regain their full vision.
In conclusion, post-traumatic vision syndrome is a serious problem that can greatly affect a person’s life. While it may take time and effort to get better, with the right help and care, people can improve their vision and get back to a normal life.
If you have PTVS, it’s important to talk to a doctor and learn about your condition and the treatments available. With hard work and a positive attitude, you can beat PTVS and have a happy and satisfying life.
Cheek out what it means to lose touch with reality or see how to get something off your mind permanently